- Amal Augustine
- February 6, 2026
Proven Strategy to Solve Spontaneity of Cell Reaction MCQs
In the context of electrochemistry, the spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs plays a crucial role in determining whether a chemical reaction can proceed without the need for external energy input. This spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs concept is fundamental to understanding how galvanic cells and electrolytic cells function, and it hinges upon the relationship between Gibbs free energy and the electrochemical potential of the cell.
The spontaneity of a cell reaction mcqs refers to the natural tendency of a reaction to occur without external influence. When a chemical reaction is spontaneous, it means that the system’s Gibbs free energy decreases, and energy is released in the process. In electrochemical terms, a spontaneous reaction is associated with a positive cell potential (E°_cell). Conversely, if the cell potential is negative, the reaction is non-spontaneous and requires an external power source to proceed.
For a cell reaction to be spontaneous, the cell potential (E_cell) must be positive. This indicates that the spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs is governed by the cell’s ability to drive the flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode. In a galvanic cell, this electron flow results in the production of electrical energy, which can be harnessed for practical use. The spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs is directly related to the electrochemical potentials of the half-reactions involved. Each half-reaction has a characteristic reduction potential (E°), and the overall cell potential is calculated as the difference between the reduction potentials of the two half-cells.
To further understand the spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs, it is essential to consider the relationship between the cell potential and Gibbs free energy (ΔG). The equation that connects these quantities is:
ΔG=−nFEcell\Delta G = -nFE_{cell}
Where:
-
ΔG is the change in Gibbs free energy,
-
n is the number of moles of electrons involved in the reaction,
-
F is the Faraday constant (96,485 C/mol),
-
EcellE_{cell} is the cell potential.
According to this equation, when the spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs is positive, the Gibbs free energy (ΔG) will be negative, indicating a spontaneous process. On the other hand, if the cell potential is negative, the reaction will have a positive Gibbs free energy change, signifying that the reaction is non-spontaneous. This relationship between Gibbs free energy and cell potential provides a quantitative means of determining whether a given electrochemical reaction will occur spontaneously.
The spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs also depends on temperature. In some cases, a reaction that is non-spontaneous at room temperature may become spontaneous at higher or lower temperatures. The temperature dependence is reflected in the Nernst equation, which adjusts the cell potential according to the temperature and concentration of reactants and products:
Ecell=E°cell−0.0592nlogQE_{cell} = E°_{cell} – \frac{0.0592}{n} \log Q
Where Q is the reaction quotient. The spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs can thus change with variations in temperature and concentration, further emphasizing the dynamic nature of electrochemical systems.
In practical applications, such as in batteries and fuel cells, the spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs is a key factor in determining the efficiency and performance of the device. For instance, the spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs in a lead-acid battery drives the discharge and recharge processes. When the cell potential is positive during discharge, the battery supplies electrical energy, and when it is negative during charging, external energy is required to reverse the reaction.
The spontaneity of cell reactions mcqs also plays a significant role in corrosion processes. For example, iron undergoes oxidation in the presence of oxygen and moisture, and this reaction is spontaneous under typical environmental conditions. This type of reaction is a manifestation of the spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs, which leads to the gradual degradation of metals.
Understanding the spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs is also crucial in the study of electrolysis, where non-spontaneous reactions are driven by the application of external electrical energy. In electrolytic cells, such as those used in electroplating or water splitting, the spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs dictates the direction of electron flow and determines the substances that are oxidized or reduced at the electrodes.
Spontaneity of Cell Reaction MCQs with Sloved Answers
-
What will be the EcellE_{cell} for the given cell?
Zn | Zn²⁺(0.1M) || Cu²⁺(0.01M) | Cu
Given: EZn2+/Zn0E^0_{Zn²⁺/{Zn}} = 0.76 V and ECu2+/Cu0E^0_{Cu²⁺/{Cu}} = 0.34 V.
Also predict whether the reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous.-
a) -1.07 V and non-spontaneous
-
b) -1.13 V and non-spontaneous
-
c) 1.13 V and spontaneous
-
d) 1.07 V and spontaneous
-
Answer: d
-
-
What will be the half-cell potential of a hydrogen electrode acting as an anode and dipped in a solution of pH = 2?
-
a) 0.059 V
-
b) 0.118 V
-
c) 0.276 V
-
d) 0.236 V
-
Answer: b
-
-
For the following cell Zn | Zn²⁺ || Cd²⁺ | Cd
EcellE_{cell} = 0.30V, Ecell0E^0_{cell} = 0.36V, then the value of [Cd2+][Zn2+]\frac {[Cd²⁺]}{[Zn²⁺]} is-
a) 10
-
b) 0.01
-
c) 0.1
-
d) 100
-
Answer: b
-
-
Calculate the standard free energy change for the reaction
2Ag + 2H⁺ → H₂ + 2Ag⁺
E°E° for Ag⁺ + e⁻ → Ag is 0.80 V-
a) 308.8 kJ
-
b) 154.4 kJ
-
c) -308.8 kJ
-
d) -154.4 kJ
-
Answer: b
-
-
The standard reduction potential of Pb and Zn electrodes are -0.126 V and -0.763 V respectively. The cell equation will be:
-
a) Pb²⁺ + Zn → Pb + Zn²⁺
-
b) Pb⁴⁺ + 2Zn → Pb + 2Zn²⁺
-
c) Zn²⁺ + Pb → Zn + Pb²⁺
-
d) None
-
Answer: a
-
-
What will be the oxidation potential for the following hydrogen half cell at 1 bar pressure and 25°C temperature?
Pt(s) | H₂(g), 1 bar | HCl(aq); pH = 3-
a) 0.059 V
-
b) 0.188 V
-
c) 0.177 V
-
d) 0.001 V
-
Answer: c
-
-
In which metal container, the aqueous solution of CuSO₄ can be stored?
ECu2+/Cu0E^0_{Cu²⁺/{Cu}} = 0.34 V
EFe/Fe2+0E^0_{Fe/{Fe}²⁺} = 0.44 V, EAl/Al3+0E^0_{Al/{Al}³⁺} = 1.66 V
ENi/Ni2+0E^0_{Ni/{Ni}²⁺} = 0.25 V, EAg−/Ag0E^0_{Ag^{-}/{Ag}} = 0.80 V-
a) Ag
-
b) Ni
-
c) Fe
-
d) Al
-
Answer: a
-
-
How long (approximate) should water be electrolyzed by passing through 100 amperes current so that oxygen released can completely burn 27.66 g of diborane?
(Atomic weight of B = 10.8μ)-
a) 6.4 hours
-
b) 8.0 hours
-
c) 3.2 hours
-
d) 1.6 hours
-
Answer: c
-
-
The electrode potential, E°E° for the reduction of MnO₄⁻ to Mn²⁺ in acidic medium is +1.51 V. Which of the following metal(s) will be oxidised? The reduction reaction and standard electrode potentials for Zn²⁺, Ag⁺, and Au⁺ are given as:
Zn²⁺(aq) + 2e⁻ → Zn(s), E°E° = -0.762 V
Ag⁺(aq) + e⁻ ⇌ Ag(s), E°E° = +0.80 V
Au⁺(aq) + e⁻ ⇌ Au(s), E°E° = +1.69 V-
a) Zn
-
b) Zn and Ag
-
c) Zn and Au
-
d) Au
-
Answer: b
-
-
The standard emf of the cell (E°cellE°_{cell}) and equilibrium constant (KeqK_{eq}) of the following reaction:
Cd²⁺ + 4NH₃ ⇌ Cd(NH₃)₄²⁺ at 298 K is
-
a) E°cellE°_{cell} = 1.0V; KeqK_{eq} = 1.26×10⁷
-
b) E°cellE°_{cell} = 0.21V; KeqK_{eq} = 1.26×10⁷
-
c) E°cellE°_{cell} = 1.0V; KeqK_{eq} = 6.60×10³³
-
d) E°cellE°_{cell} = 0.21V; KeqK_{eq} = 6.60×10³³
-
Answer: b
-
Given, ECl2/Cl−0E^0_{Cl_2/{Cl}^-} = 1.36V,
ECr3+/Cr0E^0_{Cr^3+/{Cr}} = -0.74 V
ECr2O72−/Cr3+0E^0_{Cr_2O_7^{2-}/{Cr}^3+} = 1.33V
EMnO4−/Mn2+0E^0_{MnO_4^{-}/{Mn}^2+} = 1.51V.
Among the following, the strongest reducing agent is
-
a) Cl⁻
-
b) Mn²⁺
-
c) Cr³⁺
-
d) Cr
-
Answer: d
-
The standard emf of galvanic cell involving 3 moles of electrons in its redox reaction is 0.59 V. The equilibrium constant for the reaction of the cell is
-
a) 10²⁵
-
b) 10¹⁰
-
c) 10¹⁵
-
d) 10³⁰
-
Answer: d
-
The value of reaction quotient (Q), for the following cell
Zn(s) | Zn²⁺(0.01 M) || Ag⁺ (1.25 M) | Ag(s) is
-
a) 156
-
b) 125
-
c) 1.25 × 10²
-
d) 6.4 × 10⁻³
-
Answer: d
-
The reaction is spontaneous if the cell potential is
-
a) positive
-
b) negative
-
c) zero
-
d) infinite
-
Answer: a
-
Consider the single electrode process 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ ⇌ 2H₂, catalyzed by platinum black electrode in HCl electrolyte. The potential of the electrode is -0.059 V. SHE. What is the concentration of the acid in the hydrogen half cell if the H₂ pressure is 1 bar?
4H⁺ + 4e⁻ ⇌ 2H₂
-
a) 1 M
-
b) 10 M
-
c) 0.1 M
-
d) 0.01 M
-
Answer: c
-
Consider the following electrode processes of a cell,
Cl⁻ → ½Cl₂ + e⁻ [MCl + e⁻ → M + Cl⁻]
If EMF of this cell is -1.140 V and E° value of the cell is -0.55 V at 298 K, the value of the equilibrium constant of the sparingly soluble salt MCl is in the order of
-
a) 10²
-
b) 10⁷
-
c) 10⁻⁴
-
d) 10⁻¹⁰
-
Answer: d
-
What is the standard potential of the Ti³⁺/Ti electrode?
Ti³⁺ + 2e⁻ → Ti⁺; E° = 1.26 V
Ti³⁺ + e⁻ → Ti; E° = -0.336 V
-
a) 0.924 V
-
b) -0.924 V
-
c) 0.728 V
-
d) -0.728 V
-
Answer: c
-
The standard reduction potentials of Cu²⁺/Cu and Cu²⁺/Cu are 0.337 and 0.153 volts respectively. The standard electrode potential for the Cu⁺/Cu half cell will be
-
a) 0.490 V
-
b) 0.980 V
-
c) 0.827 V
-
d) 0.521 V
-
Answer: d
-
The E° values for Mn and Zn are more negative than expected because
-
a) they have either half-filled and fully-filled configurations
-
b) they can easily donate electrons
-
c) it is quite easy to remove electrons from their orbitals
-
d) None of the above
-
Answer: a
-
For the cell reaction
Pb + Sn²⁺ → Pb²⁺ + Sn
Given that, Pb → Pb²⁺ + 2e⁻; E° = 0.13 V
Sn²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Sn; E°= -0.14 V
What would be the ratio of cation concentration for which E = 0?
-
a) 1/4
-
b) 1/2
-
c) 1/3
-
d) 1
-
Answer: b
-
Electrolytic reduction of alumina to aluminium by Hall-Heroult process is carried out:
-
a) in the presence of NaCl
-
b) in the presence of fluorite
-
c) in the presence of cryolite which forms a melt with lower melting temperature
-
d) in the presence of cryolite which forms a melt with higher melting temperature
-
Answer: c
-
In the cell represented by
Pb(s) | Pb²⁺ (1M) || Ag⁺ (1M) | Ag(s),
the reducing agent is
-
a) Pb²⁺
-
b) Ag⁺
-
c) Ag
-
d) Pb
-
Answer: d
-
The pressure of H₂ required to make the potential of H₂ electrode zero in pure water at 298 K is
-
a) 10⁻⁸ atm
-
b) 10⁻¹⁴ atm
-
c) 10⁻¹⁰ atm
-
d) 10⁻²⁰ atm
-
Answer: b
-
Given that the standard reduction potentials for M⁺/M and N⁺/N electrodes at 298 K are 0.52 V and 0.25 V respectively.
Which of the following is correct in respect of the following electrochemical cell?
M/M⁺ || N⁺/N
-
a) The standard EMF of the cell is -0.77V
-
b) The overall cell reaction is a spontaneous reaction
-
c) The standard EMF of the cell is -0.27V
-
d) The standard EMF of the cell is 0.77V
-
Answer: c
-
During electrolysis of H₂O, molar ratio of H₂ and O₂ produced is
-
a) 2:1
-
b) 1:2
-
c) 1:1
-
d) 1:4
-
Answer: a
-
The EMF of the cell Ti/Ti⁺ (0.001M) || Cu²⁺(0.01M) | Cu is 0.83. The cell EMF can be increased by
-
a) Increasing the concentration of Ti⁺ ions and Cu²⁺ ions
-
b) None of these
-
c) Increasing the concentration of Ti⁺ ions
-
d) Increasing the concentration of Cu²⁺ ions
-
Answer: d
-
The Ered0E^0_{red} value for metal A, B, and C are 0.34, -0.80, and -0.46 V respectively state the correct order for their ability to act a reducing agent
-
a) C>A>B
-
b) A>B>C
-
c) B>C>A
-
d) C>B>A
-
Answer: c
-
The EMF of a galvanic cell by coupling two electrodes M₁ | M₁²⁺(0.1M) || M₂²⁺ (0.01M) | M₂ is +1.47 V. If the E° value (reduction potential) of M₂ electrode is 0.9V, E°(reduction potential) value of M₁ electrode in volts would be
-
a) -0.57
-
b) 0.57
-
c) -0.6
-
d) 0.6
-
Answer: c
-
In an electrochemical cell anode and cathode are respectively
-
a) Positively and negatively charged ions
-
b) Positively and negatively charged electrodes
-
c) Negatively and positively charged electrodes
-
d) Negatively and positively charged ions
-
Answer: c
-
The products obtained at the cathode and anode respectively during the electrolysis of aqueous K₂SO₄ solution using platinum electrodes are
-
a) H₂, O₂
-
b) H₂, H₂SO₄
-
c) H₂, SO₂
-
d) K, SO₂
-
Answer: a
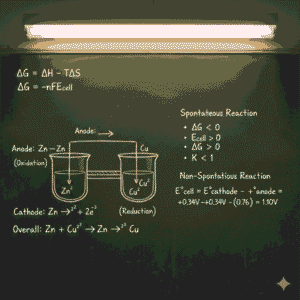
Conclusion on Spontaneity of Cell Reaction MCQs
In conclusion, the spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs is a fundamental concept in electrochemistry that determines whether a reaction will occur naturally or require external energy. By understanding spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs, the relationship between cell potential and Gibbs free energy, we can predict the behavior of electrochemical cells and apply this knowledge in various practical applications, from batteries to corrosion prevention. The spontaneity of cell reaction mcqs is influenced by the electrochemical potentials of the half-reactions, temperature, and concentration of reactants, making it a dynamic and essential factor in the study of electrochemistry.

Amal Augustine is the founder of ExQuizMe, a dynamic learning and quiz platform built to make education engaging, competitive, and fun. A passionate learner and an academic achiever, Amal completed his schooling at Government HSS Manjapra, graduating with 92.5% in Computer Science. He later earned his degree from St. Stephen’s College, University of Delhi, one of India’s most prestigious arts and science institutions.
Currently, Amal is pursuing his Master’s degree at National Sun Yat-sen University, Taiwan, where he continues to deepen his interest in research and technology. Throughout his school and college years, he won 50+ national-level interschool and collegiate quiz competitions, was
Beyond academics, Amal Augustine is an avid reader of science journals, a dedicated research student, and a technology enthusiast who loves programming and exploring the world of Computer Science. Through ExQuizMe, he aims to make learning accessible, enjoyable, and empowering for students across the globe.
