- Amal Augustine
- January 8, 2026
Master Thermodynamics Smartly : High-Impact Adiabatic Process and Carnot Engine MCQs
Adiabatic process and Carnot engine MCQs play a crucial role in understanding the fundamental laws of thermodynamics and their practical applications. An adiabatic process is a thermodynamic process in which no heat is exchanged between the system and its surroundings. Any change in the internal energy of the system during an adiabatic process occurs solely due to work done by or on the system. This adiabatic process and Carnot engine mcqs concept is commonly observed in rapid expansions and compressions, such as the bursting of a bicycle tube, propagation of sound waves in air, and expansion of gases in engines, making it a high-weightage topic in competitive exams.
Thermodynamics is one of the most concept-driven and scoring chapters in physics, playing a crucial role in competitive examinations such as NEET, JEE, and various university-level assessments. Questions based on thermodynamic processes and laws MCQs frequently test a student’s understanding of energy transfer, heat-work relations, and the behavior of gases under different physical conditions. Among these, adiabatic processes and Carnot engines mcqs, heat engines, refrigerators, and entropy form the backbone of many conceptual and numerical problems.
In adiabatic process and Carnot engine mcqs ,the adiabatic process is especially important because it represents situations where no heat exchange occurs between the system and its surroundings, such as bursting of a cycle tube, propagation of sound waves in air, or rapid expansion of gases. Similarly, the Carnot engine is a fundamental theoretical model that defines the maximum possible efficiency of any heat engine operating between two given temperatures. Adiabatic Process and Carnot engine MCQs based on Carnot cycle efficiency, refrigerator performance, and heat engines help students understand the limitations imposed by the second law of thermodynamics.
This collection of thermodynamics processes and laws MCQs is designed to strengthen conceptual clarity by covering isothermal, isobaric, isochoric, and adiabatic processes along with real-life applications like refrigerators and heat engines. Practicing such adiabatic Process and Carnot engine MCQs not only improves problem-solving speed but also builds confidence in handling tricky conceptual questions where small misunderstandings can lead to incorrect answers.The adiabatic process and Carnot engine mcqs help students understand core thermodynamics principles,improves problem-solving skills,and master second-law-based concepts for compitative exams like NEET,JEE & CUET.
30 Adiabatic Process and Carnot Engine MCQs-
1. In adiabatic expansion of gas, the quantity which remains constant is
A. Amount of heat
B. Temperature
C. Both the amount of heat and temperature
D. Pressure and temperature of gas
Answer: A
2. When gas in a vessel expands its internal energy decreases. The process involved is
A. Isothermal
B. Isobaric
C. Adiabatic
D. None
Answer: C
3. In an adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas, the product of pressure and volume
A. Decreases
B. Increases
C. Remains constant
D. First increases and then decreases
Answer: A
4. A graph of pressure versus volume for an ideal gas for different processes is shown. In the graph, curve OC represents
A. Isochoric process
B. Isothermal process
C. Adiabatic process
D. None
Answer: D
5. The temperature of the system decreases in the process of
A. Free expansion
B. Adiabatic expansion
C. Isothermal expansion
D. Isothermal compression
Answer: B
6. Bursting of cycle tube, propagation of sound waves in air, sudden blowing off of safety valve of a pressure cooker are examples of
A. Isothermal process
B. Adiabatic process
C. Cyclic process
D. Isobaric process
Answer: B
7. The process in which no heat is exchanged with the surroundings of a system is
A. Isothermal
B. Isobaric
C. Isometric
D. Adiabatic
Answer: D
8. When there is no heat change from surroundings in a system, the process taking place is
A. Isobaric
B. Adiabatic
C. Isochoric
D. Isothermal
Answer: B
9. When an ideal gas is compressed isothermally, its pressure
A. Increases
B. Decreases
C. Remains the same
D. First increases then decreases
Answer: A
10. In which of the following processes is heat neither absorbed nor released by a system?
A. Adiabatic process
B. Isobaric process
C. Isochoric process
D. Isothermal process
Answer: A
11. For an adiabatic process, the correct relation between internal energy and work done is
A. ΔU = −ΔW
B. ΔU = ΔW
C. ΔU = −ΔW in isothermal process
D. ΔU = −ΔW in adiabatic process
Answer: A
12. A process in which there is no flow of heat between system and surroundings is
A. Adiabatic process
B. Cyclic process
C. Isobaric process
D. Isochoric process
Answer: A
13. Expansion during heating
A. Increases the weight of a material
B. Decreases density of material
C. Occurs only in solids
D. Occurs at same rate in liquids and solids
Answer: B
14. There is no change in internal energy of an ideal gas when it undergoes
A. Isothermal expansion
B. Adiabatic expansion
C. Free expansion
D. Isobaric expansion
Answer: C
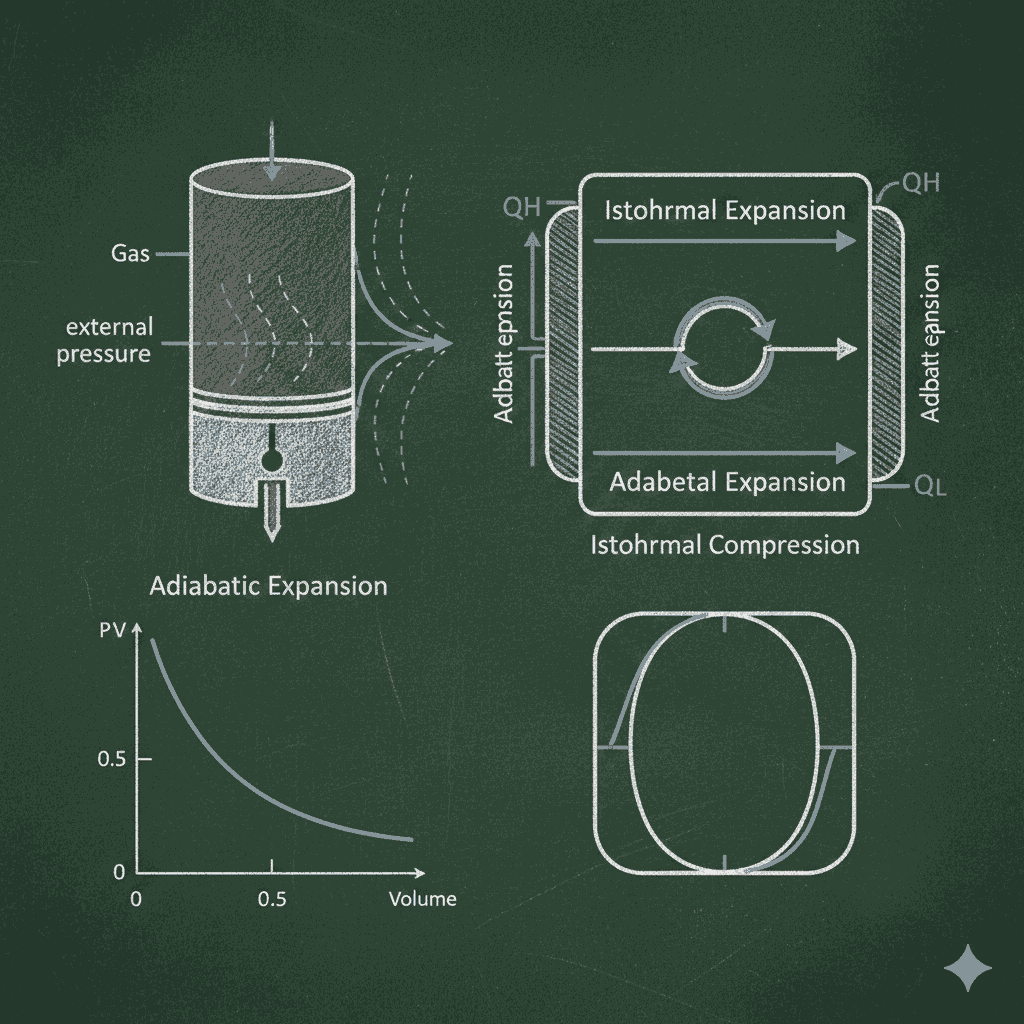
15. The Carnot cycle of a two-reservoir heat engine consists of
A. One isothermal and two adiabatic processes
B. Two isothermal and one adiabatic process
C. Two isothermal and two adiabatic processes
D. Two isobaric and two isothermal processes
Answer: C
16. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A. All reversible cycles have same efficiency
B. Reversible cycles are more efficient than irreversible ones
C. Carnot cycle is reversible
D. Carnot cycle has maximum efficiency
Answer: A
17. A heat engine is a device
A. That converts mechanical energy into heat energy
B. That converts heat energy into mechanical energy
C. That absorbs heat from sink and gives to source
D. None of these
Answer: B
18. The freezer in a refrigerator is located at the top so that
A. Entire chamber cools quickly due to convection
B. Motor is not heated
C. Heat gained is high
D. Heat gained is low
Answer: A
19. Carnot engine works between 300 K and 400 K and delivers 800 J work. Heat supplied is
A. 2400 J
B. 3200 J
C. 1200 J
D. 3600 J
Answer: B
20. A thermoelectric refrigerator works on
A. Joule effect
B. Seebeck effect
C. Peltier effect
D. Thermionic effect
Answer: C
21. If the refrigerator door is kept open, the room gets
A. Cooled
B. Heated
C. No effect
D. Uncertain
Answer: B
22. When a heater is switched off, it cools to room temperature because
A. It only radiates heat
B. It only absorbs heat
C. It first loses heat then absorbs radiation
D. None
Answer: C
23. Efficiency of Carnot engine
A. Independent of source and sink temperatures
B. Independent of working substance only
C. Can be 100%
D. None
Answer: B
24. Work done by gas in the given process is
A. Positive
B. Negative
C. Zero
D. Cannot be determined
Answer: B
25. Refrigerator cannot cool a room when door is open because it violates
A. First law of thermodynamics
B. Second law of thermodynamics
C. Conservation of momentum
D. Conservation of energy
Answer: B
26. If refrigerator door is kept open, room temperature will
A. Increase
B. Decrease
C. Remain constant
D. Uncertain
Answer: A
27. Efficiency of Carnot engine is
A. 1 − (T₁ − T₂)
B. 1 − T
C. (T₂ − T₁)⁻¹
D. 1 − (T₂ / T₁)
Answer: D
28. Correct statement about refrigerator coefficient of performance (β)
A. β is higher when temperature difference is smaller
B. β is always less than 1
C. β increases due to ice formation
D. Defrosting decreases β
Answer: A
29. Carnot engine works between 527°C and 200 K. Heat absorbed is
A. 12 × 10⁶ J
B. 16 × 10⁶ J
C. 3 × 10⁶ J
D. 20 × 10⁶ J
Answer: B
30. During phase change, entropy
A. Remains constant
B. Always increases
C. Always decreases
D. May increase or decrease
Answer: D
Conclusion on Adiabatic Process and Carnot Engine MCQs
Mastering adiabatic process and Carnot engine MCQs is essential for gaining a solid grasp of thermodynamics as a whole. These adiabatic Process and Carnot engine mcqs questions repeatedly appear in physics examinations because they test a student’s ability to connect physical laws with real-world phenomena such as heat engines, refrigerators, and entropy changes. Understanding why internal energy changes during adiabatic expansion, why Carnot efficiency depends only on temperature limits, and why a refrigerator cannot cool a room with its door open reflects true conceptual learning.
Practicing thermodynamic processes and laws MCQs, students develop a clear distinction between isothermal, adiabatic, isobaric, and isochoric processes and learn how work, heat, and internal energy are interrelated. Questions related to Adiabatic process and Carnot engine mcqs along with entropy ,strongly reinforce the importance of the second law of thermodynamics in setting natural limits on energy conversion. Solving MCQs on the adiabatic process and Carnot engine mcqs builds strong insight into deal heat engine behaviour and energy conservation, which are key pillars of thermodynamics questions in competitive exams.
By practicing adiabatic process and Carnot engine MCQs, learners strengthen their grasp of thermodynamic cycles, energy conservation, and entropy concepts. These adiabatic process and Carnot engine MCQs are essential for exams like NEET, JEE, and board-level physics, as they bridge theoretical laws with real-world thermal machines. Mastery of these adiabatic process and Carnot engine mcqs topics builds a strong foundation for advanced studies in thermodynamics and engineering applications.
In conclusion, consistent practice of these adiabatic Process and Carnot engine MCQs, combined with a strong understanding of underlying concepts, ensures better performance in exams and a deeper appreciation of thermodynamics. Whether preparing for competitive exams or strengthening core physics knowledge, focusing on adiabatic processes and Carnot engine MCQs will significantly enhance conceptual accuracy and exam readiness.

Amal Augustine is the founder of ExQuizMe, a dynamic learning and quiz platform built to make education engaging, competitive, and fun. A passionate learner and an academic achiever, Amal completed his schooling at Government HSS Manjapra, graduating with 92.5% in Computer Science. He later earned his degree from St. Stephen’s College, University of Delhi, one of India’s most prestigious arts and science institutions.
Currently, Amal is pursuing his Master’s degree at National Sun Yat-sen University, Taiwan, where he continues to deepen his interest in research and technology. Throughout his school and college years, he won 50+ national-level interschool and collegiate quiz competitions, was
Beyond academics, Amal Augustine is an avid reader of science journals, a dedicated research student, and a technology enthusiast who loves programming and exploring the world of Computer Science. Through ExQuizMe, he aims to make learning accessible, enjoyable, and empowering for students across the globe.
